Abstract
Background:Myc has proven extremely difficult to target therapeutically. Therefore, we hypothesized that optimal inhibition of multiple key pathways involved in Myc expression could overcome this long-standing problem. We identified aurora A kinase (AURKA) and bromodomain protein (BRD)4 as therapeutic targets to counteract Myc deregulation based on strong evidence that these pathways are essential for tumor maintenance in Myc-driven malignancies.
Methods: Cytotoxicity assays using MTS and trypan blue were used to compare levels of drug sensitivity in lymphoma cell lines with high and low Myc mRNA expression. Apoptosis and cell cycle assays were performed using Annexin V and Propidium Iodide staining. Cycloheximide chase followed by immunoblotting was used to examine Myc protein degradation kinetics, and real-time RT-PCR was used to examine Myc mRNA levels. Murine xenograft models were used to assess the efficacy and tolerability of single vs. combined inhibition.
Results: Myc-overexpressing Burkitt lymphoma (Raji) cells were treated with increasing concentrations of small molecule inhibitors against AURKA (MLN-8237), BRD4 (I-BET-151), or both drugs for 48 to 72 hours and cell viability was evaluated. MLN-8237 and I-BET-151 inhibited cell growth individually with IC-50 of 10 nM, and 650 nM, respectively. As compared to treatment with the single agent alone, dual treatment induced more significant cell growth inhibition with IC-50 achieved at drug concentrations of < 5 nM and 500 nM for MLN-8237 and I-BET-151, respectively. The combination index (CI) values were less than 1 at various drug concentrations, indicating that different combinations were synergistic in terms of inhibitory effect on tumor cell viability. Superior activity of the dual inhibition was also noted in different Myc-overexpressing lymphoma cells. Combination treatments increased apoptosis and induced more pronounced cell cycle arrest compared to the single agent treatment alone.
We then analyzed protein expression by Western blot. MLN-8237 reduced the expression of p-HisH3 and p-AURKA while increasing the expression of p-S6K. Treatment with I-BET-151 resulted in significant reduction of Myc total protein. Cycloheximide chase experiments demonstrated that inhibition of AURKA increased the rate of Myc protein degradation, while BRD4 inhibition had no effect on degradation kinetics. Conversely MLN-8237 did not decrease Myc transcription, while I-BET-151 significantly reduced the levels of Myc mRNA. The combination of the two drugs demonstrated additive/synergistic decreases of both Myc protein degradation and Myc transcription at higher drug doses.
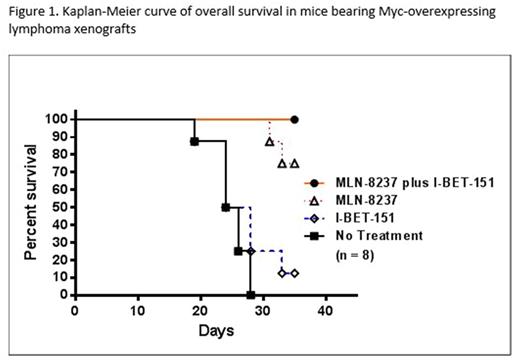
Lastly, athymic nude mice bearing Ramos lymphoma xenografts were treated with MLN-8237, I-BET-151, or with the combination of both agents (n = 8 per group). The mean tumor volumes in mice treated with negative control, I-BET-151, and MLN-8237 as single agents were 3480, 2320, and 671 mm3, respectively, at Day 28. Mice treated with MLN-8237/I-BET-151 combinations had mean tumor volume of 461 mm3 at Day 28. The survival rates for mice treated with negative control, I-BET-151, and MLN-8237 as single agents were 0%, 10%, and 70%, respectively, at Day 35 (Figure 1). Mice treated with the MLN-8237 and I-BET-151 combination demonstrated a 100% survival rate at Day 35.
Conclusion: Our data demonstrated that Myc-overexpressing lymphoma can be successfully targeted by inhibition of Myc transcription and/or enhancement of Myc protein degradation. Specifically, MLN-8237, a small molecule inhibitor against AURKA, induced apoptosis of Myc-overexpressing tumor cells in vitro and showed the most promising anti-tumor activity in mice bearing Myc-overexpressing lymphoma, especially when combined with I-BET-151, a BRD4 inhibitor.
Park: Cornerstone Pharmaceuticals: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Gilead: Speakers Bureau; Seattle Genetics: Research Funding; Teva: Consultancy, Research Funding; Takeda: Research Funding. Ghosh: TG Therapeutics: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Pharmacyclics: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Jassen: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Kite Pharma: Consultancy, Honoraria; AbbVie: Consultancy, Honoraria, Speakers Bureau; Seattle Genetics: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Gilead: Consultancy, Honoraria, Speakers Bureau; Bristol Myers Squibb: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Celgene: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau. Sharpless: Unity Biotechnology: Other: NA; HealthSpan Diagnostics: Other: NA; Pfizer: Other: NA; G1 Therapeutics: Equity Ownership.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal